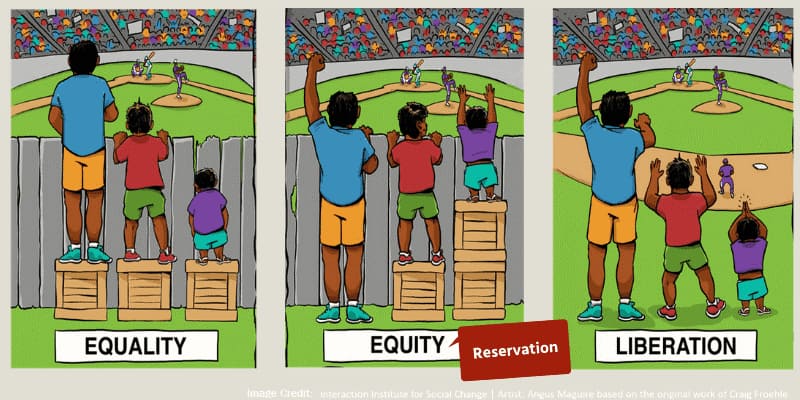
The reservation system in India has been a contentious issue since its inception. The system was introduced to address historical injustices and provide opportunities to marginalized communities. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the reservation system in India and its constitutional basis.
Introduction
India is a diverse country with a complex social hierarchy. The caste system has played a significant role in shaping the society, with those at the bottom of the hierarchy facing discrimination and marginalization. The reservation system was introduced to address this issue and provide opportunities to those who were historically disadvantaged.
Constitutional Basis
The reservation system in India is based on the Constitution of India, which guarantees equality of opportunity and prohibits discrimination on the basis of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. The Constitution provides for reservation in education, employment and political representation to the Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
The reservation system is enshrined in Articles 15(4) and 16(4) of the Constitution. Article 15(4) allows the state to make special provisions for the advancement of socially and educationally backward classes, while Article 16(4) provides for reservation in public employment.
Reservation in Education
The reservation system in education is aimed at providing access to higher education to marginalized communities. The reservation in education is provided in government-funded institutions, including universities, colleges, and schools.
- Certificate Course in Labour Laws
- Certificate Course in Drafting of Pleadings
- Certificate Programme in Train The Trainer (TTT) PoSH
- Certificate course in Contract Drafting
- Certificate Course in HRM (Human Resource Management)
- Online Certificate course on RTI (English/हिंदी)
- Guide to setup Startup in India
- HR Analytics Certification Course
The reservation percentage varies from state to state, with some states providing up to 50% reservation to SCs, STs, and OBCs. The Supreme Court has upheld the reservation system in education and has stated that it is essential to ensure equal opportunities for all.
Reservation in Employment
The reservation system in employment is aimed at providing equal opportunities to marginalized communities in public sector jobs. The reservation in employment is provided in government jobs and in educational institutions.
The reservation percentage for SCs, STs and OBCs in public sector jobs is 15%, 7.5% and 27%, respectively. The reservation percentage for persons with disabilities is 4%.
Reservation in Political Representation
The reservation system in political representation is aimed at ensuring that marginalized communities are adequately represented in the political sphere. The reservation in political representation is provided in local bodies, state assemblies, and parliament.
The reservation percentage for SCs, STs and OBCs in local bodies and state assemblies is 50%, while the reservation percentage for SCs and STs in parliament is 84 seats out of the total 543 seats.
Criticism
The reservation system in India has faced criticism on various grounds. One of the main criticisms is that it has led to reverse discrimination and has created a divide among different communities. Some argue that the reservation system is not based on economic criteria, and hence, it has benefited only a few privileged castes and not the truly marginalized communities.
Conclusion
The reservation system in India has been a subject of debate and controversy. However, it has played a significant role in providing opportunities to marginalized communities and ensuring that they are adequately represented in education, employment, and politics. The reservation system is based on the constitutional principle of social justice and is essential to address historical injustices. However, there is a need for continuous review and evaluation of the reservation system to ensure that it is effective in achieving its goals and does not lead to reverse discrimination.
- Certificate Course in Labour Laws
- Certificate Course in Drafting of Pleadings
- Certificate Programme in Train The Trainer (TTT) PoSH
- Certificate course in Contract Drafting
- Certificate Course in HRM (Human Resource Management)
- Online Certificate course on RTI (English/हिंदी)
- Guide to setup Startup in India
- HR Analytics Certification Course